Soap manufacturers introduce the main ingredients of soap
by:Jingliang
2023-09-10
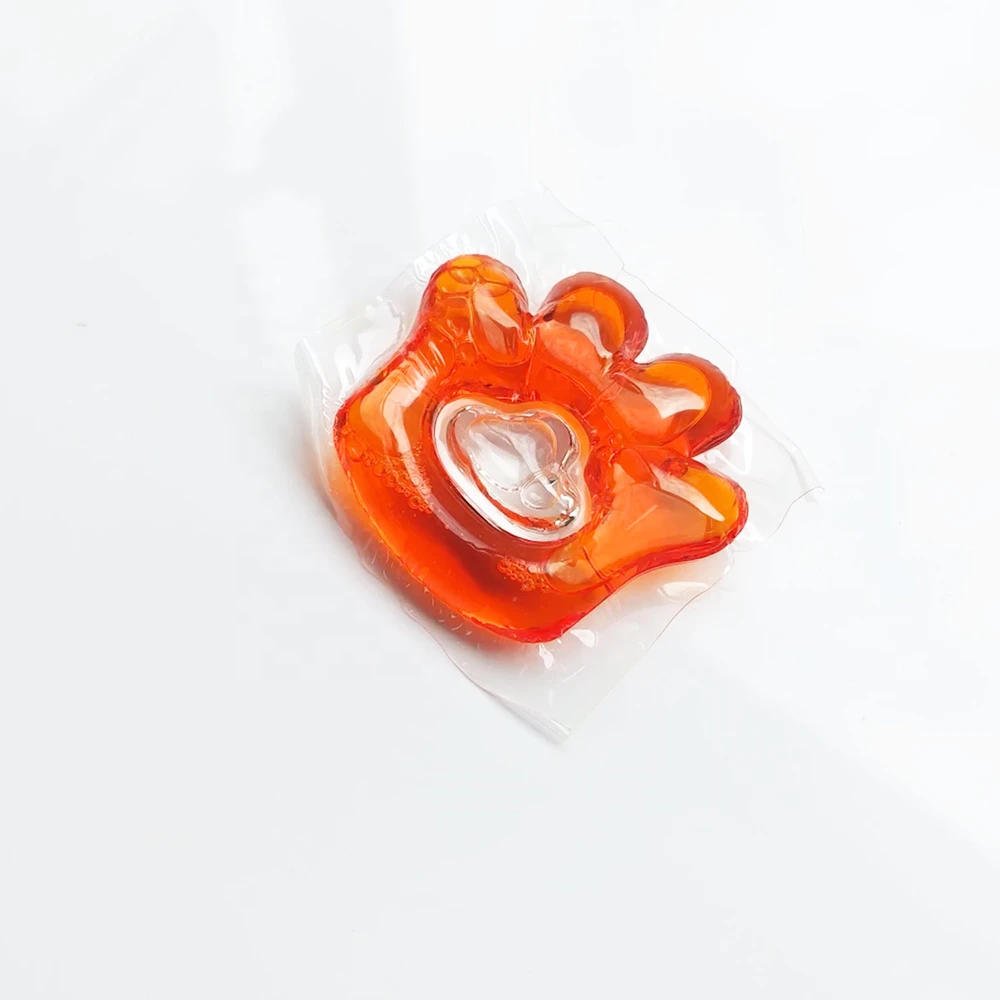
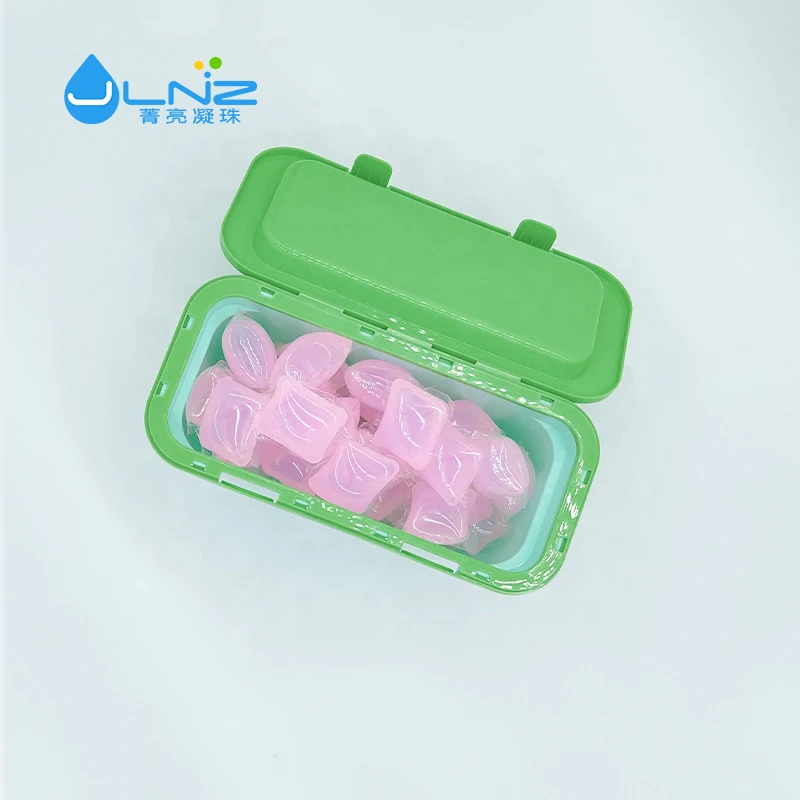
Soap processed soap is a general term for fatty acid metal salts. The carbon number of fatty acids in daily soaps is generally 10-18. The metals are mainly alkali metals such as sodium or potassium, and are also made from ammonia and some organic bases such as ethanolamine and triethanolamine. into special purpose soaps. Soap includes laundry soap, toilet soap, metal soap, liquid soap, and related products fatty acid, hardened oil, glycerin, etc. 1. Composition of soap: sodium salt R-CO2Na of carboxylic acid, synthetic pigment, synthetic fragrance, preservative, antioxidant, foaming agent, hardener, viscous agent, synthetic surfactant. 2. The main component of soap is R-CO2Na, (sodium stearate (C17H35COONa)), wherein the R groups are generally different and are various hydrocarbon groups. R- is a hydrophobic group, and a carboxyl group is a hydrophilic group. In hard water, soap and Ca2+, Mg2+, etc. form curd-like substances, fatty acid calcium salts, etc., which are commonly called 'calcium soaps' and become useless descaling agents. Adding softeners to hard water removes the hard water ions, allowing the soap to work. 3. The main ingredients are sodium stearate, and its molecular formula is C17H35COONa (carbon 17 hydrogen 35 + carbon + oxygen + oxygen + sodium) (it can also be written as RCOONa, which is produced by the reaction of sodium hydroxide [NaOH] and alkali synthetic oil) . 4. The molecular structure of soap can be divided into two parts. One end is a charged polar COO- (hydrophilic site), and the other end is a non-polar carbon chain (lipophilic site). Soap can destroy the surface tension of water. When soap molecules enter the water, the polar hydrophilic part will destroy the attraction between water molecules and reduce the surface tension of water, so that the water molecules are distributed evenly in the surface to be cleaned. Clothing or skin surface. 5. The lipophilic part of the soap penetrates deep into the oil stain, while the hydrophilic part dissolves in water. The combination forms smaller oil droplets after agitation, and the surface is covered with the hydrophilic part of the soap, instead of re-aggregating to form. Big oil stain. This process (also known as emulsification) is repeated several times, and all oil contamination becomes very tiny oil droplets that dissolve in water and can be easily rinsed off. Soap processing consultation website: https://www.jingliang-pod.com/
Custom message